Luminometers play a crucial role in a wide array of scientific applications, ranging from biomedical research to environmental monitoring. They are sophisticated devices designed to measure light emitted by samples undergoing chemiluminescent or bioluminescent reactions. According to recent industry reports, the global luminometer market is expected to reach a valuation of over $500 million by 2025, driven by advancements in diagnostic techniques and the growing trend of personalized medicine. Among the various variants available in the market, the photonmaster luminometer stands out for its efficiency and reliability in delivering accurate luminescence measurements.
The functioning of a photonmaster luminometer is based on the principle of photon detection, which enables researchers to quantify biological and chemical interactions with remarkable precision. These devices utilize advanced sensor technology that captures the emitted light, allowing for real-time analysis and data collection. The expected growth of the luminometer market aligns with the increasing need for high-throughput screening in drug discovery and development, further amplifying the significance of tools like the photonmaster luminometer in modern laboratories. As research and industrial sectors continue to evolve, the understanding and application of luminometry will remain integral to innovation and scientific progress.
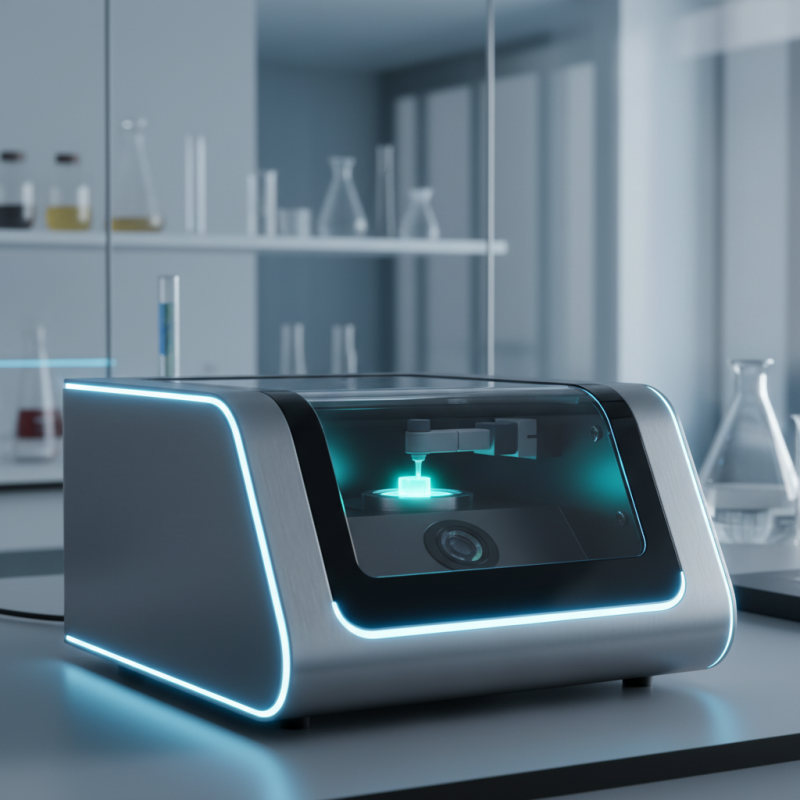

A luminometer is an essential instrument in scientific research that measures light emissions produced by biochemical reactions. It is particularly valuable in fields such as biochemistry, molecular biology, and pharmaceuticals, where researchers analyze luminescence for applications like detecting cellular activity and determining concentrations of substances. The primary purpose of a luminometer is to provide accurate and sensitive measurements to help scientists understand biological processes and interactions at a molecular level.
In many research applications, luminometers can be used to measure the luminescence of chemical reactions involving luciferase enzymes, which emit light when they interact with specific substrates. This ability makes luminometers crucial for assays such as ATP detection, enzyme activity studies, and gene expression analysis. With increasing advancements in technology, modern luminometers now offer enhanced sensitivity and faster read times, enabling researchers to conduct high-throughput screening with greater efficiency.
Tips: When selecting a luminometer for research, consider factors like sensitivity, measurement range, and ease of use. Remember to keep the instrument calibrated and routinely maintain it to ensure reliable results. Additionally, familiarize yourself with different luminescence assays and their protocols to optimize your experimental outcomes and enhance reproducibility in your research.
Luminometry is a scientific technique primarily focused on measuring light intensity. This method is crucial in various fields, including bioluminescence studies, environmental monitoring, and pharmaceutical research. The fundamental principle behind luminometry involves the quantification of light emitted during chemical reactions, often associated with the presence of specific compounds. This process is typically carried out using sophisticated instruments known as luminometers, which detect and measure the photons emitted in these reactions.
In recent years, advancements in luminometric technology have enhanced sensitivity and accuracy, enabling researchers to detect low levels of light with greater precision. According to a report by the International Society for Luminescence, the global luminometry market is projected to grow annually by approximately 5.5% over the next five years, driven by increasing applications in clinical diagnostics and environmental assessments. The ability to measure minute quantities of bioluminescent signals has made luminometers invaluable in areas such as drug discovery and gene expression analysis, where detecting minimal changes can lead to significant insights.
Understanding the principles of luminometry is not only essential for optimizing laboratory results but also for broadening the applications of light measurement in various scientific disciplines. The combination of photodetection techniques and the growing need for accurate light measurement systems is catalyzing innovations in luminometry, which continue to evolve as technology advances.
The Photonmaster Luminometer is an advanced device designed for measuring light emissions, specifically in luminescence applications. Understanding its key components helps users appreciate how accurate and reliable results are obtained in various biological and chemical assays. At the heart of the Photonmaster is the photodetector, which captures light emitted during reactions. This sensor plays a critical role in translating light signals into measurable data, allowing for precise quantification of luminescent reactions.
Another essential component is the optical filter system, which ensures that only the specific wavelengths of light relevant to the measurement reach the detector. This enhances the sensitivity and selectivity of the device, making it highly effective for diverse applications, including drug development and environmental monitoring. Additionally, the luminometer features a robust data processing unit that analyzes the captured signals and delivers results in real-time, expediting the decision-making process in laboratory settings.
Tips for optimal use of the Photonmaster Luminometer include regularly calibrating the device to maintain accuracy and ensuring that the optical components are clean to avoid interference with light measurements. Also, familiarizing oneself with the user interface can significantly improve efficiency in data acquisition and analysis, allowing researchers to focus on their experiments rather than troubleshooting the equipment.
The operational mechanism of a luminometer primarily revolves around its ability to measure luminous intensity produced by bioluminescent reactions or chemiluminescence. The device utilizes specific light detectors that are sensitive to the wavelengths emitted during these chemical reactions. When a luminescent substrate interacts with an enzyme or a chemical compound, it produces light, which is then captured by the photodetector within the luminometer. The amount of light detected is proportionate to the intensity of the reaction, allowing for quantitative analysis.
Inside the luminometer, the sample is placed in a designated vial or chamber where the chemiluminescent reaction takes place. Upon initiation, the emitted photons travel through a light-tight compartment to ensure that no external light interferes with the measurements.
The detector converts the light into an electrical signal, which is subsequently analyzed by the device’s built-in software. This software often compiles data into readable formats, providing users with real-time insights on the intensity of the luminescent reaction, thereby facilitating experiments in fields such as molecular biology, pharmacology, and environmental monitoring.
Luminometers are sophisticated devices used to measure luminescence, a process where light is produced by a chemical reaction. In various fields, luminometers like the Photonmaster serve as essential tools for quantifying light emitted during biochemical reactions, facilitating innovative research and applications. One of the primary applications is in the realm of biotechnology, where these devices support assay development, enabling researchers to evaluate cellular responses to drugs, gene expression, and protein interactions through bioluminescent and chemiluminescent signals.
Another significant area of application is environmental monitoring. Luminometers can detect and quantify light emitted from microbial activity in water and soil samples, allowing scientists to assess the presence of pollutants or the health of ecosystems. In the field of food safety, these instruments are invaluable for monitoring cleanliness and contamination levels by measuring light produced from microbial assays on food surfaces. This versatility underscores the importance of luminometers in diverse sectors, from healthcare to environmental science, highlighting their role in advancing both research and practical applications.





